Businesses rely on data analysts to uncover trends, solve problems, and drive smarter decisions—especially in data-heavy. From streamlining IT operations to boosting conversion rates through predictive modeling, the impact of data analysis is measurable and strategic. To stand out in this results-driven field, reviewing strong data analyst resume examples can help you demonstrate the right mix of technical skills, analytical thinking, and business insight.
This guide features real-world samples tailored to different experience levels. It also includes tips for optimizing resume sections, aligning with job descriptions, and ensuring ATS-friendliness. Whether you’re a fresh graduate or a seasoned analyst, you’ll find actionable advice to improve your resume and catch the attention of hiring managers.
Data Analyst Resume Examples
Each career level has unique demands. Let’s explore sample formats and strategies for entry-level, mid-level, and experienced data analysts.
Entry-Level Data Analyst
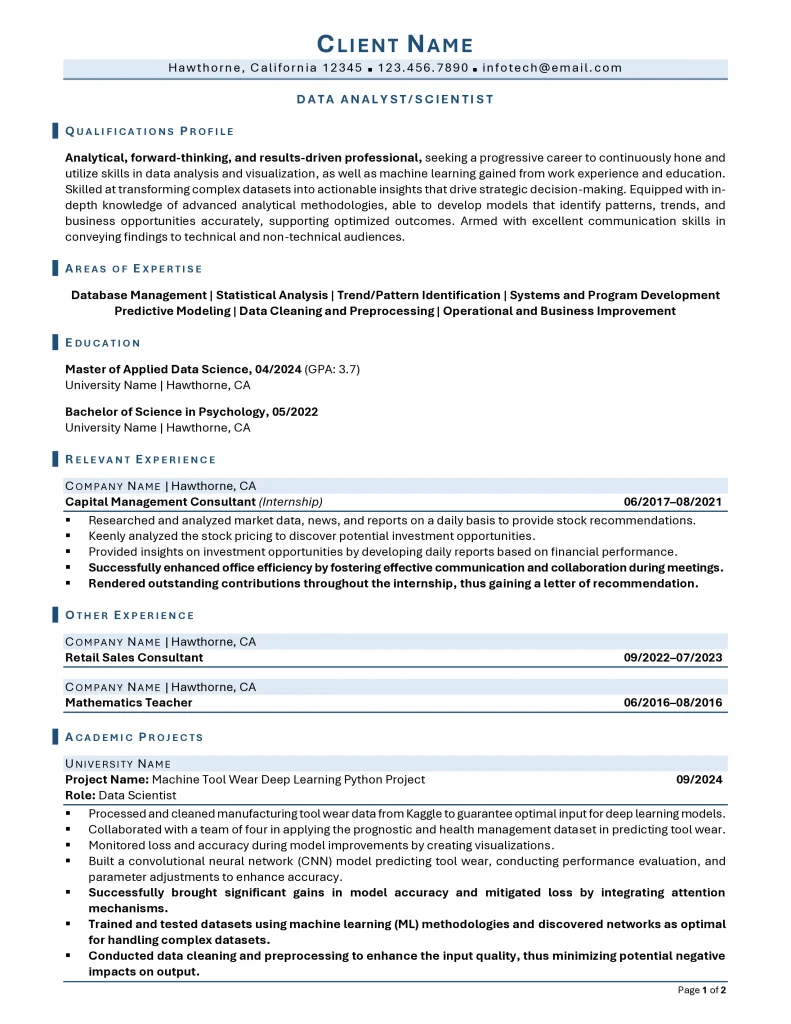

Download a copy of the Entry-Level Data Analyst Resume Example
Intermediate-Level Data Analyst
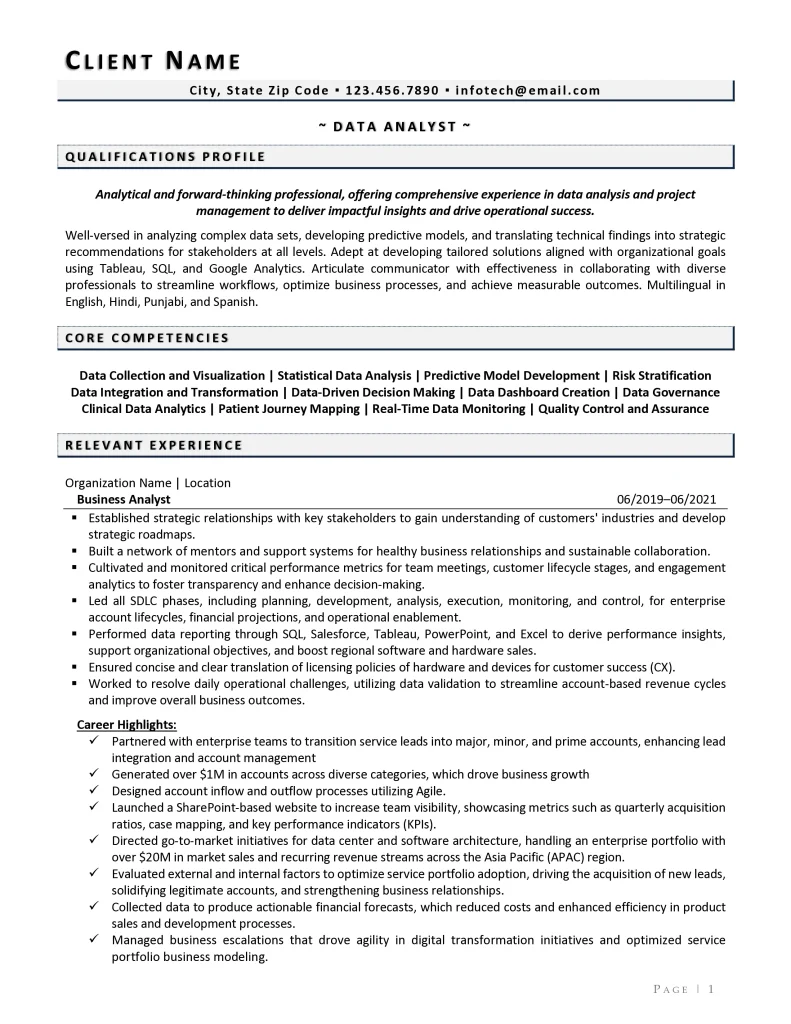


Download a copy of the Intermediate Level Data Analyst Resume Example
Experienced Data Analyst
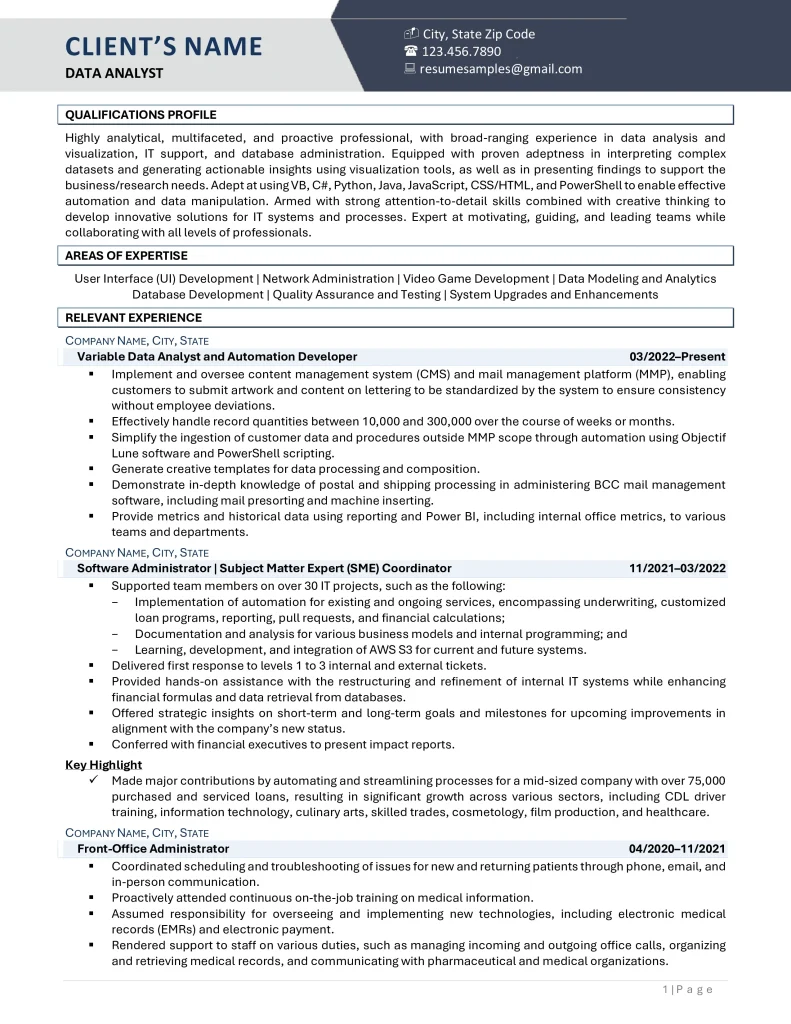
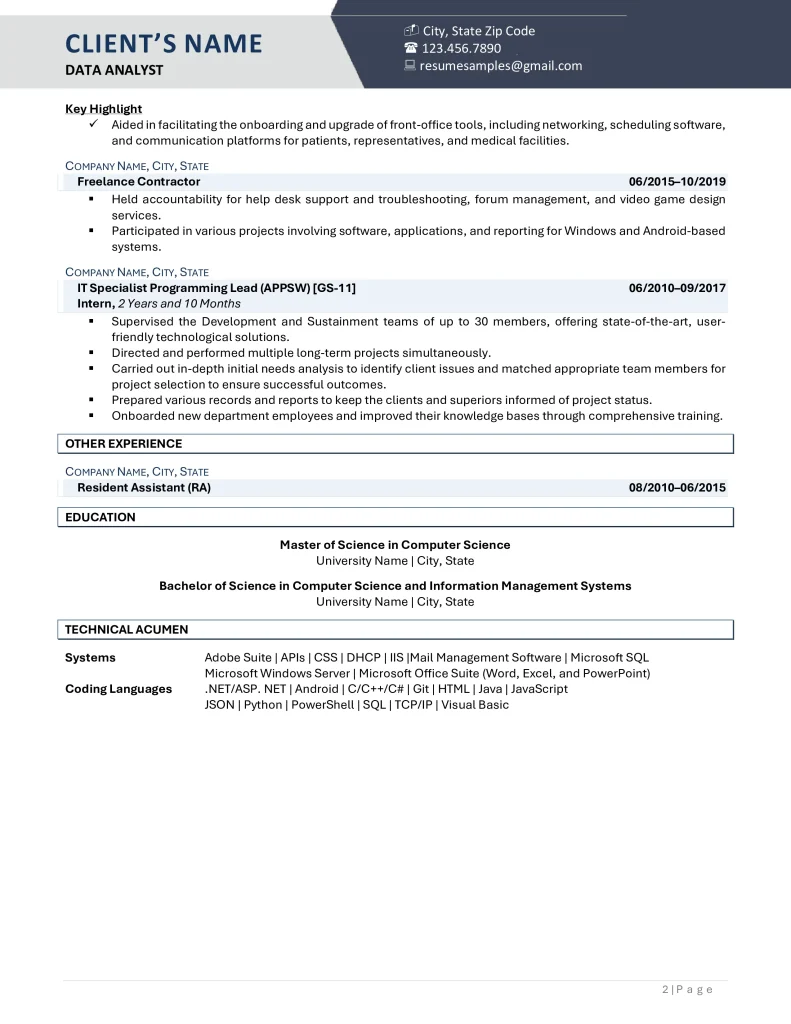
Download a copy of the Experienced Data Analyst Resume Example.
Key Responsibilities to Highlight
When writing your data analyst resume, focus on showcasing real-world impact. Here are core responsibilities hiring managers look for:
- Analyzing data from various sources such as CRMs, ERP systems, and customer databases.
- Improving process times through automation or data pipeline optimization.
- Conducting predictive modeling to anticipate trends and guide decision-making.
- Creating dashboards and reports to support key business functions.
- Collaborating with stakeholders to define KPIs and metrics.
- Ensuring data accuracy and integrity through regular audits and validation checks.
- Presenting findings in a clear, actionable format for both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Supporting data governance efforts by maintaining documentation and data standards.
Essential Resume Sections Every Data Analyst Should Include
A well-organized resume helps hiring managers quickly assess your qualifications, especially in technical roles. When reviewing data analyst resume examples, you’ll notice that standout resumes share several consistent sections that showcase both hard and soft skills clearly. Here’s how to structure yours:
1. Summary of Qualifications
This section gives a quick overview of your background, tools you excel in, and the value you bring. Tailor it to the role you’re applying for, using concise and impactful language.
Example: “Data analyst with 4 years of experience using SQL, Tableau, and Python to drive business decisions across e-commerce and finance.”
2. Areas of Expertise
Highlight your core technical competencies and domain knowledge. This section should be keyword-rich to pass ATS scans and immediately show where your strengths lie.
Example: “Data Cleaning, Predictive Modeling, Dashboard Creation, A/B Testing, SQL, Python, Excel, Tableau”
3. Relevant Work Experience
Detail your past roles with a focus on achievements and measurable results. Use bullet points to emphasize your contributions, tools used, and how your work impacted business outcomes.
Example: “Reduced report generation time by 40% by designing automated templates in Tableau.”
4. Projects
Include academic, freelance, or side projects that show your practical abilities. This section is especially valuable for entry-level candidates or those making a career switch.
Example: “Developed a predictive model using Python to estimate customer churn with 87% accuracy.”
5. Education
List your academic background, including degrees, institutions, and graduation dates. If you hold a Bachelor of Science in Statistics, be sure to include relevant coursework that supports your analytical skills.
Example: “B.S. in Statistics, XYZ University – Coursework: Regression Analysis, Data Mining, Probability Models”
6. Certifications
Certifications add credibility and show initiative in skill-building. Focus on credentials that align with the job description and current industry standards.
Examples: Google Data Analytics Certificate, Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate, Tableau Desktop Specialist

Tips for Writing an ATS-Friendly Data Analyst Resume
To ensure your resume makes it past applicant tracking systems and into the hands of recruiters:
- Quantify Your Achievements: Whenever possible, include numbers to show the impact of your work, such as “reduced processing time by 30%” or “improved report accuracy by 15%.” Quantifiable results grab hiring managers’ attention and demonstrate your effectiveness.
- Tailor Your Resume for Each Application: Customize your resume to highlight skills and experiences most relevant to the specific job you’re applying for. This shows recruiters you’ve carefully read the job description and match their needs.
- Keep It Concise and Relevant: Focus on the most important details that demonstrate your qualifications and avoid including unrelated information. A clear and focused resume improves readability and keeps hiring managers engaged.
- Use Action Verbs: Start bullet points with strong action verbs like “analyzed,” “developed,” or “automated” to emphasize your contributions. This approach makes your resume more dynamic and impactful.
- Proofread Thoroughly: Ensure your resume is free from typos, grammatical errors, and formatting inconsistencies. A polished resume reflects your attention to detail and professionalism, both critical for a data analyst role.
ATS bots scan data analyst resumes for specific patterns and terms. Clean formatting and keyword optimization can dramatically increase your visibility in LinkedIn searches and online applications.
Top Skills for a Data Analyst Resume
Demonstrating the right mix of technical and interpersonal abilities is essential to stand out in a competitive job market. Your resume should reflect the skills that align with industry demands and show your capacity to deliver results through data-driven solutions.
Data Cleaning and Preparation
Cleaning and preparing data is essential for ensuring accuracy and consistency in analysis. This involves handling missing values, standardizing formats, and structuring raw datasets for analysis-ready use.
Statistical Programming (R, Python)
Proficiency in R and Python allows data analysts to perform complex statistical analyses and automate tasks. These languages are widely used for data manipulation, modeling, and visualization.
Data Visualization (Tableau, Power BI)
Creating clear and interactive dashboards in tools like Tableau and Power BI helps translate raw data into actionable insights. Effective visualization allows stakeholders to quickly understand patterns and trends.
Machine Learning (Basic Models)
Understanding basic machine learning models enables analysts to create predictions and detect patterns. This includes implementing algorithms like linear regression, decision trees, and clustering methods.
SQL and Relational Databases
SQL is fundamental for querying structured data stored in relational databases. Analysts use SQL to extract, filter, join, and analyze data efficiently from multiple sources.
Big Data Tools (Spark, Hadoop)
Familiarity with tools like Apache Spark and Hadoop is valuable for handling large-scale data processing tasks. These platforms enable analysts to process massive datasets quickly and reliably.
Report Automation
Automating reports reduces manual effort and increases consistency. Using tools like Python scripts, Excel macros, or Tableau scheduling can streamline recurring reporting tasks.
Communication and Presentation
Effective communication ensures insights are clearly conveyed to both technical and non-technical audiences. Strong presentation skills help drive data-driven decisions with clarity and confidence.
Critical Thinking
Data analysts must critically evaluate data sources, methodologies, and outcomes. This involves questioning assumptions and ensuring analytical results are valid and reliable.
Attention to Detail
Precision is key in identifying patterns, inconsistencies, and trends within datasets. A strong attention to detail helps prevent costly errors in analysis and reporting.
Problem-Solving
Analysts use data to identify root causes and propose evidence-based solutions. This skill is vital when dealing with ambiguous data challenges or uncovering hidden insights.
Business Acumen
Understanding business goals helps analysts frame their work in context. Business acumen allows analysts to align data insights with strategic objectives and prioritize impactful metrics.
Teamwork and Collaboration
Collaboration with cross-functional teams—from engineering to marketing—is critical for project success. Strong interpersonal skills support a productive, data-informed workplace.
Highlighting both types of skills and tying them to quantifiable outcomes can demonstrate your full range of value to potential employers.

Take the Next Step in Your Data Analytics Career
Crafting standout data analyst resume examples requires more than listing tools—it’s about telling a story of how you’ve turned data into results. From tailoring your resume to the job description, to including real-world achievements and keywords like “reduced data processing time by 30%,” these strategies ensure your resume is relevant, impressive, and interview-ready.
Ready to land your next data analyst job? Let our expert IT resume writers help you build a polished, ATS-optimized resume that showcases your analytical prowess. Whether you’re starting out or moving up, we’ll align your resume with industry demands and make sure it speaks directly to hiring managers. Contact us today to get started.




